谈谈计算机的RTC电路和IO编程的汇编指令。
这两天在github.com上写代码,出了几个例子。
其中有两个汇编语言编的是时钟代码。
这两个例子可以显示系统时钟内存的数据内容。
一个是利用BIOS的中断,一个是利用DOS中断。
这两个汇编程序主要是利用汇编语言的两个指令对I/O口通讯。
一个是 in al,71,一个是 out 70,al
70,和 71端口是系统的时钟IO通讯口。还有72和73也有同样效果。
在虚拟机上测试了,还有,通过低级的端口控制,发现我的电脑主板X79
72,73这个端口是无效果的。
实际显示可以从00h-FF显示完全从80以后是重复00-7F的数据的。
如果资料是正确的话,说明这些可能有些端口只能设置一次。还是BIOS设置的。
一个是直接显示芯片RAM。一个是映射RAM。
这个RTC时钟端口,也保存了系统其它未公开信息,只作简单说明。
;我对CMOS时钟数端口的理解 ;时钟设置端口在实模式下是端口70/71,72/73 ;CMOS的时钟有两种模式DV0=0模式,DV0=1模式 ;端口70模式是只读模式,端口71模式是只写模式 ;0e-3f 是RAM 50字节用户空间 ;40-7f 是RAM 64字节用户空间 ;80-ff 是128字节RAM扩展用户空间 ;*00-ff 是256字节RAM用户空间* ;DV0=1模式下 50 = +offset 80(DV0=0下的80) ;---------------------------------------------- ;DV0=1模式可用地址 ;00 秒 ;01 秒警 ;02 分 ;03 分警 ;04 时 ;05 时警 ;06 星期数据 ;07 月数据 ;08 月 ;09 年 ;0a 寄存器 A ;0b 寄存器 B ;0c 寄存器 C ;0d 寄存器 D ;32 是辅助国家时区(DV0=0) ;48 是国家时区代码(DV0=1) ;50 是扩展内存端口地址 ;53 是护展内存端口数据 ;7e 计数复位 ;注:秒警,分警,时警相当于闹钟的意思 ;--------------------------------------------- ;地址00 数值为00-59 当 0b 寄存器 B = 1 时 设置 ;地址00 数值自动被硬件更新,软设置停止 ;地址01 高位为C(字节[7:6]=11b)使用 ;地址01 位设置为1不使用 ; 02-03,04-05 性质同上 ; 04区别数值为00-23 ; 06数值01-07 星期日值为1 ; 07数值01-28 软件设置后自动停止 ; 08数值01-12 同上 ; 09数值00-99 同上 ;++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ;寄存器 A 字节[3:2:1:0] ; 0 0 0 0 默认最快设置 ; 0 0 0 1 256Hz(3.90625微秒) ; 0 0 1 0 128Hz(7.8125 ; 0 0 1 1 8.192kHz(122.070毫秒 ; 0 1 0 0 4.096kHz(244.141毫秒 ; 0 1 0 1 2.048kHz(488.281毫秒 ; 0 1 1 0 1.024kHz(976.5625毫秒 ; 0 1 1 1 512Hz(1.953125微秒 ; 1 0 0 0 256Hz(3.90625微秒 ; 1 0 0 1 128Hz(7.8125微秒 ; 1 0 1 0 64Hz(15.625微秒 ; 1 0 1 1 32Hz(31.25微秒 ; 1 1 0 0 16Hz(62.5微秒 ; 1 1 0 1 8Hz(125微秒 ; 1 1 1 0 4Hz(250微秒 ; 1 1 1 1 2Hz(500微秒 ;寄存器 A 字节[:4]DV0 = 0 或 1 端口72/73访问256字节RAM内存 ;地址7f 字节[:0]为1可以访问RTC内存
还有英文资料,这资料是几十年前的。现在的只是补充。
00 RTC seconds 01 RTC seconds alarm 02 RTC minutes 03 RTC minutes alarm 04 RTC hours 05 RTC hours alarm 06 RTC day of week 07 RTC day of month 08 RTC month 09 RTC year 0A RTC Status register A: RTC Status Register A bit0-3: rate selection Bits for divider output frequency (set to 0110 = 1.024kHz, 976.562鎠) bit4-6: 22 stage divider, time base being used; (initialized to 010 = 32.768kHz) bit7: 1=time update in progress, 0=time/date available 0B RTC Status register B: RTC Status Register B bit0: 1=enable daylight savings, 0=disable (default) bit1: 1=24 hour mode, 0=12 hour mode (24 default) bit2: 1=time/date in binary, 0=BCD (BCD default) bit3: 1=enable square wave frequency, 0=disable bit4: 1=enable update ended interrupt, 0=disable bit5: 1=enable alarm interrupt, 0=disable bit6: 1=enable periodic interrupt, 0=disable bit7: 1=disable clock update, 0=update count normally 0C RTC Status register C (read only): RTC Status Register C (read only) bit0-3: reserved (set to 0) bit4: update ended interrupt enabled bit5: alarm interrupt enabled bit6: periodic interrupt enabled bit7: IRQF flag 0D RTC Status register D (read only): RTC Status Register D (read only) bit0-6: reserved (set to 0) bit7: 1=CMOS RAM has power, 0=CMOS RAM has lost power 0E Diagnostic status byte: Diagnostic Status Byte bit0-1: reserved bit2: 1=time is invalid, 0=ok (POST validity check) bit3: 1=fixed disk 0 failed initialization, 0=ok bit4: 1=memory size doesn't match config info, 0=ok bit5: 1=invalid config info found, 0=ok (see below) bit6: 1=config record checksum is bad, 0=ok bit7: 1=RTC lost power, 0=power state stable 0F Shutdown status byte: 0 soft reset or unexpected shutdown 1 shut down after memory size determination 2 shut down after memory test 3 shut down with memory error 4 shut down with boot loader request 5 JMP DWORD request with INT init 6 protected mode test 7 passed 7 protected mode test 7 failed 8 protected mode test1 failed 9 block move shutdown request A JMP DWORD request without INT init 10 Diskette drive type for A: and B: Diskette drive type for A: and B: bit0-3: second diskette type bit4-7: first diskette type 0000 no drive installed 0001 DSDD 48 TPI drive 0010 DSQD 96 TPI drive other values are reserved 11 Reserved 12 Fixed disk drive type for drive 0 and drive 1 Diskette drive type for A: and B: bit0-3: second hard disk drive code (0000=no disk) bit4-7: first hard disk drive code (0000=no disk) 13 Reserved 14 Equipment byte Equipment byte bit0: 1=diskette drives installed, 0=none bit1: 1=math coprocessor installed, 0=none bit2-3: unused bit4-5: primary display bit6-7: number of diskette drives installed Bits Bits 54 Primary Display 76 Number of Drives 00 reserved 00 1 diskette drive 01 40 column color 01 2 diskette drives 10 80 column color 10 reserved 11 monochrome 11 reserved 15 LSB of system base memory in 1k blocks 16 MSB of system base memory in 1k blocks 17 LSB of total extended memory in 1k blocks 18 MSB of total extended memory in 1k blocks 19 Drive C extension byte (reserved AT) 1A Drive D extension byte (reserved AT) 1B 13 bytes reserved 2E CMOS checksum of bytes 10h-20h (MSB) 2F CMOS checksum of bytes 10h-20h (LSB) 30 LSB of extended memory size found above 1 megabyte during POST 31 MSB of extended memory size found above 1 megabyte during POST 32 Date century byte in BCD ( BIOS interface to read and set) 33 Information flags (set during power-on) Information Flags bit0-5: reserved bit6: initial setup message flag bit7: 1=IBM 128k expansion installed, 0=none 34 12 bytes reserved Programming Considerations: Write CMOS address to read or write to port 70h Read/write port 71h to get/set data - the information here is only applicable to AT and PS/2 systems - INT 1A is used to read/set the Time of Day and Alarm. To use the alarm, INT 4A must be a valid interrupt service routine. - configuration settings are maintained using the Motorola MC146818 Real Time Clock. Each of this chips 64 memory registers is used for storage (0-3F). - Bit 5 of the diagnostic (0Eh) status byte is set during a power on test. This Bit is set if no floppy disks are found or the display doesn't match the system display switch setting. - all addresses sent to port 70h have Bits 7&6 clear since Bit 7 of port 70h is used to enable/disable NMI. Setting this Bit 7 enables NMI, clearing this Bit disables NMI. - when masking the NMI through using port 70H, port 71H should be read immediately after or the RTC may be left in an unknown state. This wont affect the PS/2 watchdog timer or system channel timeout.
这是英文说明,可以对照我的注释看,英文不作翻译,只是让大家了解。
这是CMOS的RAM内存区,实际扩展后可以显读256字节。事实上,各个型号和芯片组的电路组合是不相同,但是总体一样的。
上表是常用数据已经公布了二十多年,为什么没相关的研究资料和项目,因为486 DX 440之后扩展了数据。
在486DX之前一直关注这个数据,因为那时的BIOS是只读的,之后就可写BIOS了。而自己为了生活也在做其它事情。
这是公开的数据,不过资料不太好找,所以贴到这里了。网上还是找得到的。
我的项目:http://github.com/wafer333/bootinfo 项目
---------------------------------------------------------------------
1eLKx8Cp1blSVEMgUE28xLTmxvc1ZS81Zr/JtsHE2sjdoaM=
1eLA772ru+G808jrw9jD3M7EtbW12Na3o6zQ6NKqwfTR1KOswfTR1LK7uau/qqGjA==
---------------------------------------------------------------------
以上是数据结构。
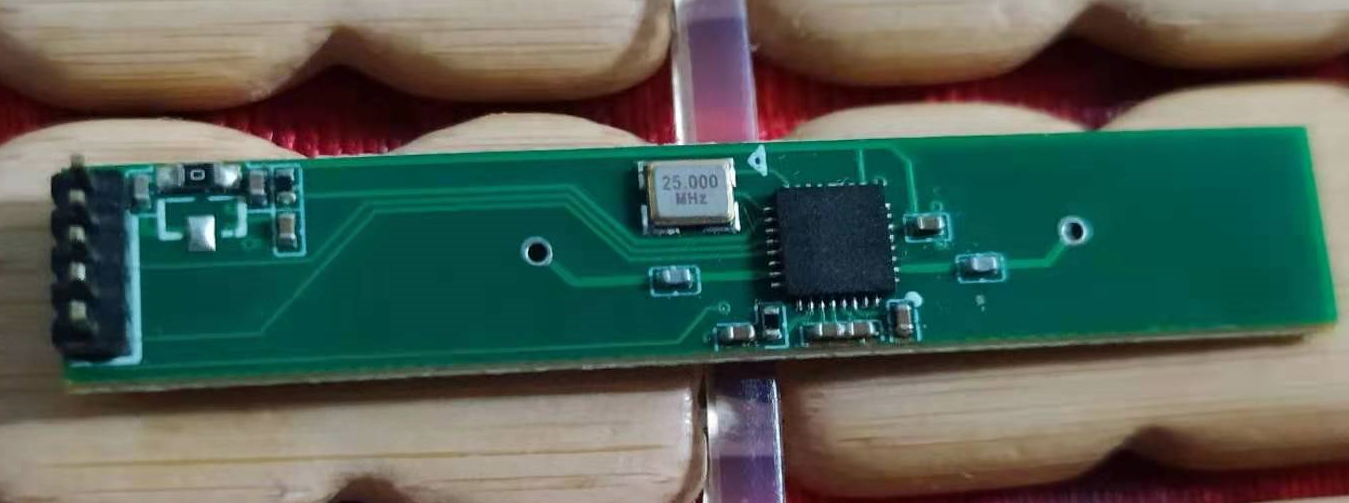
X79的主板电路图
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1eLA78u1w/e1xMrHxMfXz8mr1LK149eiw/e1xLXnwre+zcrHUlRDtefCt6O
sxuTW0NPQzPW/ydLUzai5/bzTyMXQxbrFo6zWu734sruz9qGjy7XD983is
r/OtNaqyeixuL/J0tS4xNC0Q01PU7K/t9Y=
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
这紫色小圆点指示的就是RTC电路
再说一下汇编的指令 in和out.
这个指令是传递IO口数据的,所以使用方法很简单。
但是要知道输入输出口的设备是各不相同的。
所以一个设备一个用法,有的设备本身有设备的BIOS不过计算机CPU看不到设备指令。
有的设备会挂一个中断程序,由设备BIOS自带,或者在计算机的BIOS中。
我说的设备BIOS又叫火线也叫firware,也叫固件。
如果直接用汇编控制IO设备,那就用in,out。不过还要知道设备的延迟,因为设备运转比CPU慢。
IO地址新计算机可以是0x-0xffff,这条电路总线是和内存总线不一样的,不直接访问。
IO地址在计算机中是特定和固定的。一个硬件一个地址,不可以变化。【这太重要】
简单说明一下,因为这不是一本书可以说清楚的。贴个IO地址表就明白了。
这是基本的8位常用IO地址表,当然,还有12位的和16位的地址表,设备很多,本网站有篇文章是USB设备地址,可以参考。
有的地址的数据是索引值,每个值控制着数据的数据。举个例子。
mov al,2eh
out 70h,al
然后
in al, 71h
2e值是索引值。
在一些端口中,两次
in al,71h
in al,71h
值是不一样的,这个要注意。
如果外设反应到 al,的字节是 FFh
注意了,设备正忙,CPU要有耐心等待,或者做别的工作,由int 中断程序完成。
上面x79的每根IO线路的设备会在特殊的情况下使能。让CPU工作。【说得浓缩了点】
未尽资料,简介到这里了。。。。
贴上测试代码。boch 2.7下通过。
format binary as 'img' org 7c00h ;测试代码开始 ;读时间 start: mov ax,cs mov ds,ax mov es,ax mov al,56h mov dx,0xcd6 out dx,al mov dx,0xcd7 in ax,dx and ax,111111111011111b out dx,ax mov al,57h;设置PM Reg 0x57[5]=1 mov dx,0cd6h out dx,al mov dx,0cd7h in al,dx and al,0100000b;AltCmosMapEn out dx,al mov al,24h;AcpiMMioEn mov dx,0cd6h out dx,al mov dx,0cd7h in ax,dx and ax,11b;AcpiMMioDecodeEn=1 AcpiMMioSet=1 I/O-mapped 空间 out dx,ax;[31:13] FED8_00 mov al,0ah out 70h,al in al,71h and al,110000b out 71h,al mov al,7fh out 70h,al mov al,1 out 71,al mov cx,0ffh mov al,0h mov di,data1 mov si,data1 s0: out 70h,al push ax in al,71h stosb pop ax inc al dec cx jnz s0 mov ax,0 a1: push ax call printnum1 mov al,":" int 10h mov al," " int 10h mov cx,16 call n15 pop ax inc ax cmp ax,16 jl a1 jmp $ nop mov si,data1 mov di,si ;=================== mov dx,15 n0: push dx mov cx,16 call n15 pop dx dec dx jnz n0 jmp $ n15: call printnum loop n15 mov ax,0e0dh int 10h mov ax,0e0ah int 10h ret printnum: lodsb printnum1: push ax sar al,4 call dnum mov ah,0eh int 10h pop ax call dnum mov ah,0eh int 10h mov ax,0e20h int 10h ret dnum: and al,0fh cmp al,0ah jl d1 add al,7h d1: add al,30h ret screen: mov si,data2 mov al,byte [si] call write jz write_done jmp screen write_done: xorah,ah;暂停键功能 int16h;BIOS键盘中断 loop write_done write: movah,0eh;字符终端显示输出功能函数号 mov bx,0003h;显示属性 (weird...) .more: lodsb;读到al一个字节 oral,al jz.done int10h;BIOS显示中断 jmp.more;重复.more这段代码 .done: retn data1db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h db 0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h,0h data2db 'Super blue fruit tech',0dh,0ah,0 rb 7C00h+512-2-$;fill up to the boot record signature db 055h,0AAh;the signature itself






 鄂公网安备42010402000303号
鄂公网安备42010402000303号